Service Binding
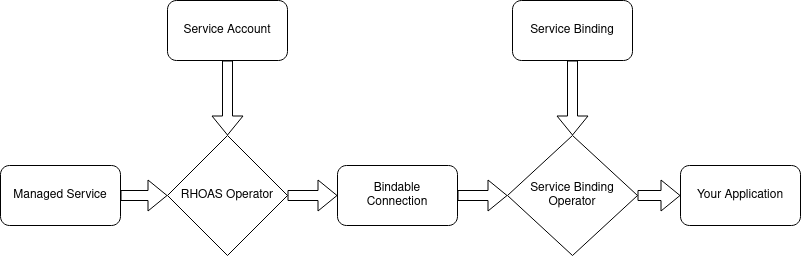
When you’re developing an application that uses multiple services (such as Kafka and a Service Registry), you normally have to manually configure connections to these services in a configuration file. These connection configurations often include public data such as well-known URLs, as well as private data such as passwords and account IDs. Custom resources (CRs) managed by the RHOAS Operator provide service binding annotations. This allows the Service Binding Operator (SBO) to expose connection information to your application. Because the SBO manages the connection information, the information stays securely inside your OpenShift cluster instead of being shared across different configuration files in source control.
The RHOAS Operator works with the SBO by setting values in the status subresource of KafkaConnection and ServiceRegistryConnection objects. These values match the values in the binding annotations. This method allows the Service Binding Operator to inject values from the CRs for these objects into end-user workloads.
Annotation Details
The service binding annotations can be found in the the KafkaConnection and ServiceRegistryConnection custom resource definitions (CRDs).
Shown below are the service binding annotations in a CR for a ServiceRegistryConnection object:
annotations:
service.binding/registryUrl: 'path={.status.registryUrl}'
## Additional binding metadata required for Quarkus
service.binding/type: 'path={.status.metadata.type}'
## OAUTH BEARER credentials
service.binding/clientId: >-
path={.status.serviceAccountSecretName},objectType=Secret,sourceKey=client-id
service.binding/clientSecret: >-
path={.status.serviceAccountSecretName},objectType=Secret,sourceKey=client-secret
service.binding/oauthTokenUrl: 'path={.status.metadata.oauthTokenUrl}'These annotations instruct the SBO to map the fields registryUrl, type, clientId, clientSecret, and oauthTokenUrl to properties provided by the ServiceRegistryConnection object, as well as references to properties stored securely in a secret. In this case, the client credentials are actually resolved by a secret lookup, using the value of .status.serviceAccountSecretName.
Likewise, the CR for a KafkaConnection object has the following service binding annotations:
.kafkaconnection.example.yaml
annotations:
service.binding/bootstrapServers: 'path={.status.bootstrapServerHost}'
## SASL PLAIN credentials
service.binding/user: >-
path={.status.serviceAccountSecretName},objectType=Secret,sourceKey=client-id
service.binding/password: >-
path={.status.serviceAccountSecretName},objectType=Secret,sourceKey=client-secret
## SASL OAUTH BEARER credentials
service.binding/clientId: >-
path={.status.serviceAccountSecretName},objectType=Secret,sourceKey=client-id
service.binding/clientSecret: >-
path={.status.serviceAccountSecretName},objectType=Secret,sourceKey=client-secret
service.binding/saslMechanism: 'path={.status.metadata.saslMechanism}'
service.binding/securityProtocol: 'path={.status.metadata.securityProtocol}'
## Additional binding metadata required for Quarkus
service.binding/type: 'path={.status.metadata.type}'
service.binding/provider: 'path={.status.metadata.provider}'Similar to the annotations in a ServiceRegistryConnection CR, the annotations in a KafkaConnection CR allow the SBO to map the fields bootstrapServers, user, password, clientId, clientSecret, saslMechanism, securityProtocol, type, and provider binding values to properties provided by the KafkaConnection object.
Binding Example
For a deployment named kafka-avro-schema-quickstart-app and a ServiceRegistryConnection object called quickstart-service-registry, the following ServiceBinding resource can be used to bind the Service Registry connection information into the pods of the deployment. The application in the deployment can look these properties up as values in the file system, or use a Quarkus extension to automatically consume them.
apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: movies
namespace: default
spec:
application:
group: apps
name: kafka-avro-schema-quickstart-app
resource: deployments
version: v1
bindAsFiles: true
services:
- group: rhoas.redhat.com
version: v1alpha1
kind: ServiceRegistryConnection
name: quickstart-service-registryConclusion
In the preceding examples, we focused on the ServiceRegistryConnection object, but the information (minus implementation details) is the same for KafkaConnection objects as well. If you want to learn more about service binding, you should look at the link{https://redhat-developer.github.io/service-binding-operator/userguide/intro.html}[Service Binding Operator documentation] and the link{https://github.com/servicebinding/spec}[Service Binding Specification for Kubernetes].