Installing Service Binding Operator
The Service Binding Operator can be installed on the following version of Kubernetes and OpenShift:
Installing on Kubernetes
You can install the Service Binding Operator using one of the following methods:
-
Installing the Service Binding Operator using Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM)
Procedure-
Go to OperatorHub.io.
-
Click on the blue Install button.
-
Follow the instructions to install the Service Binding Operator.
-
-
Installing the Service Binding Operator without OLM
Procedure-
Install the Service Binding Operator using the released resources:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/redhat-developer/service-binding-operator/releases/latest/download/release.yaml
-
Installing the Service Binding Operator from the OpenShift Container Platform web UI
-
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform installed.
-
Navigate in the web console to the OperatorHub page and type
Service Bindinginto theFilter by keywordbox: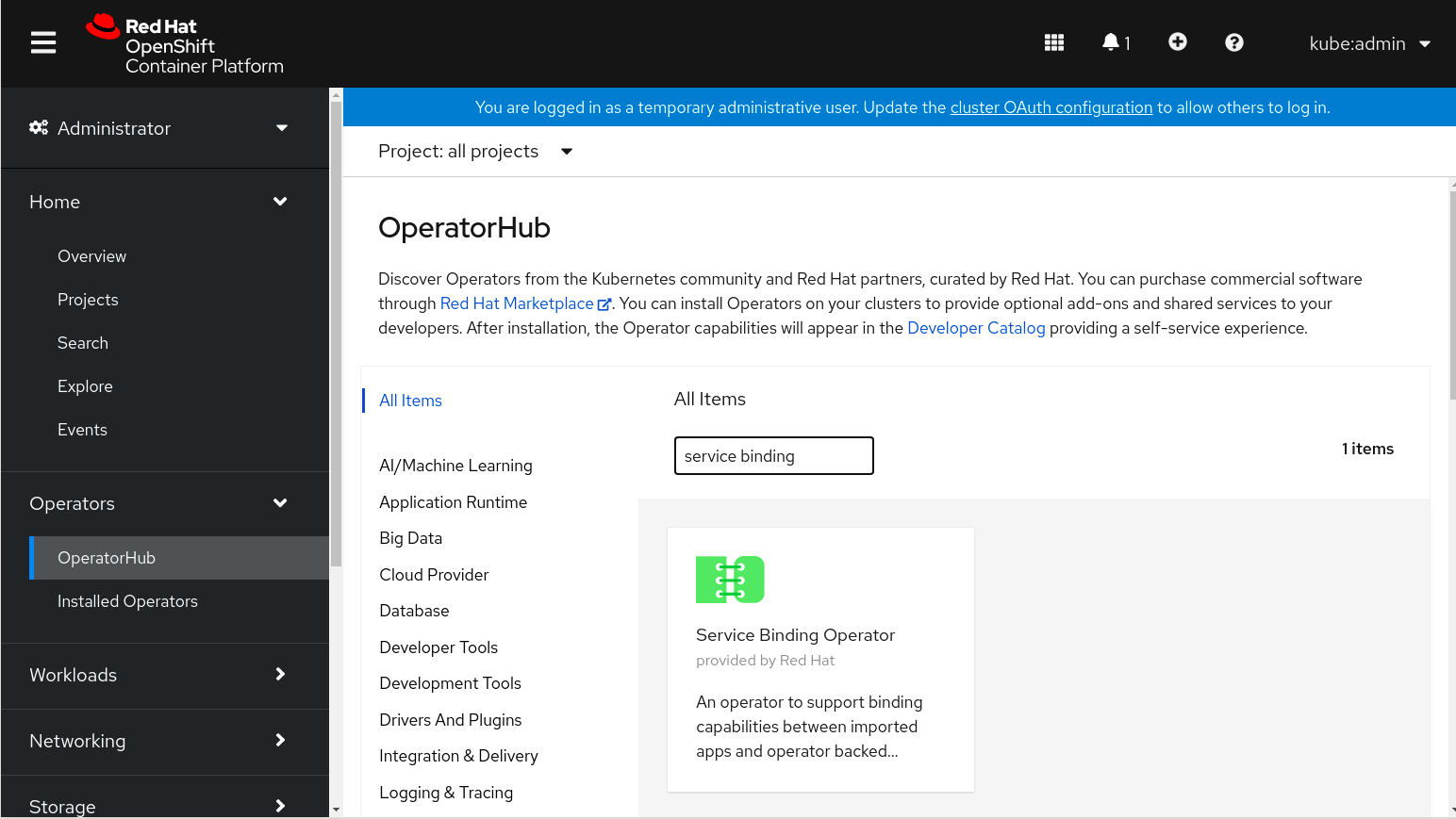
-
Click Service Binding Operator from the result. A page to install the Operator is displayed with additional information about the Operator.
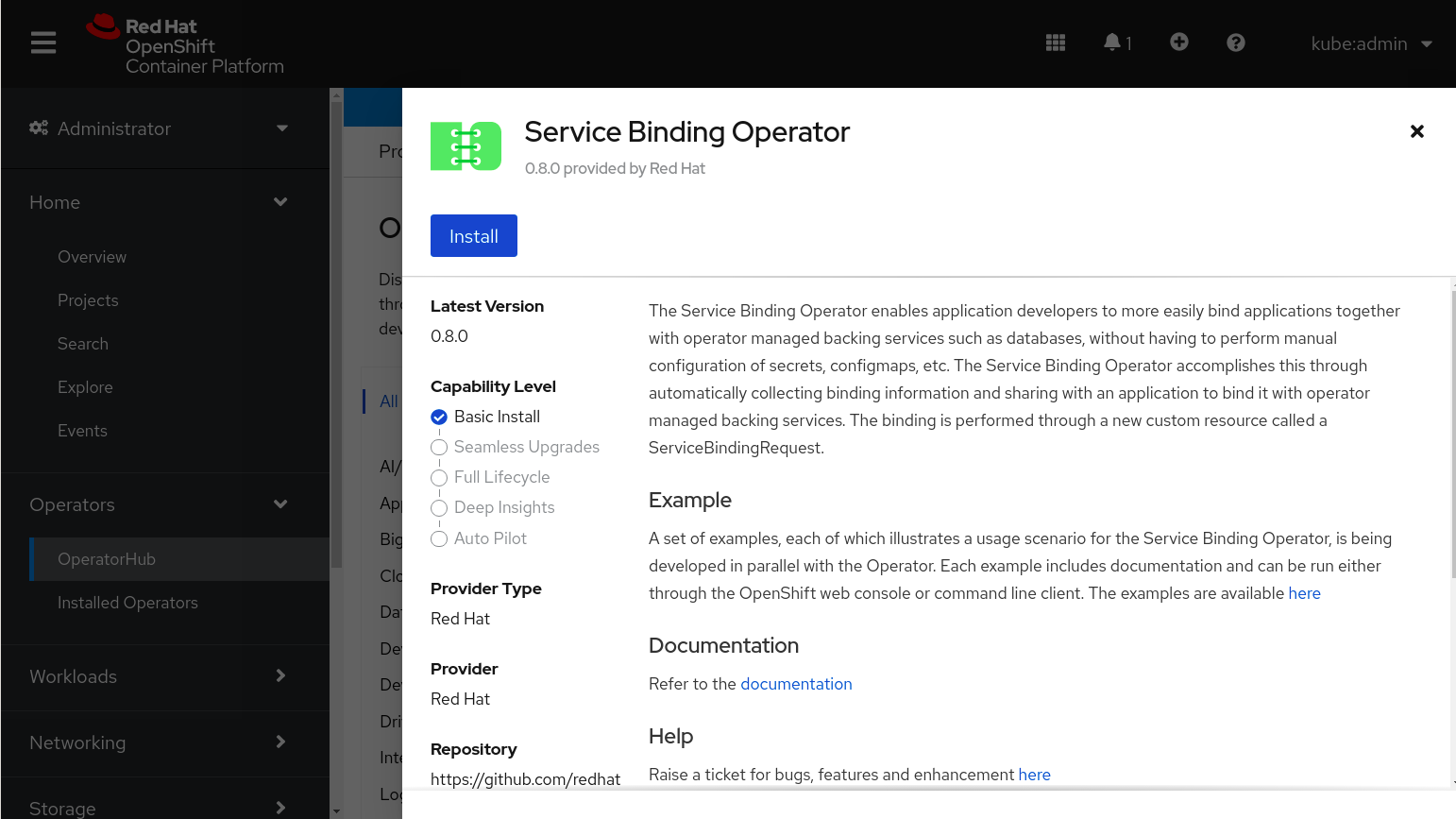
-
Click Install. The Install Operator page is displayed.
-
Select the options as per your requirements and click Install. After the installation is complete, a page with the Installed Operator – ready for use message is displayed.
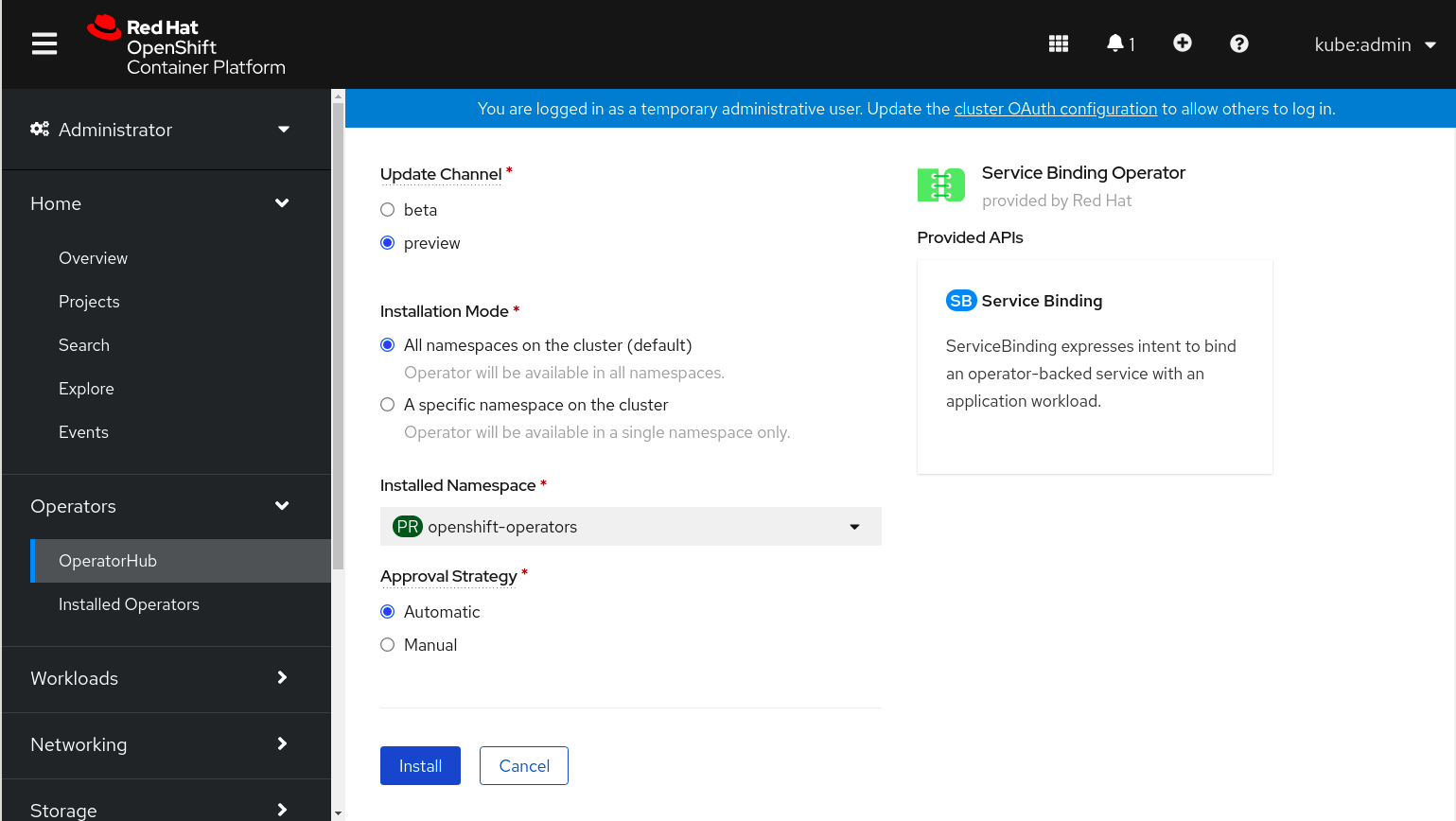
-
Click View Operator. The Service Binding Operator page is displayed with the Operator details.
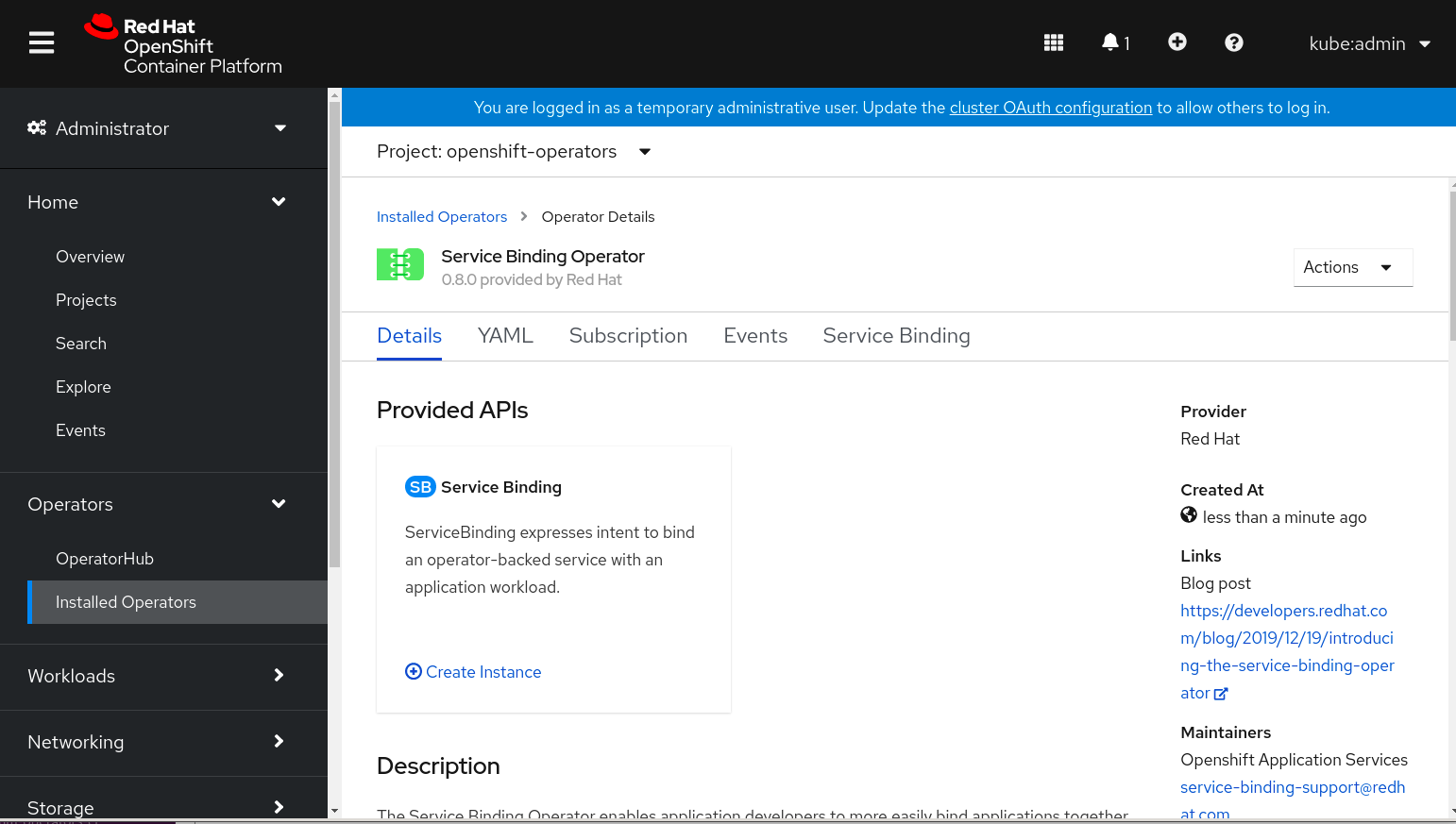
Installing the Service Binding Operator using Helm chart
The Helm chart installation involves the following steps:
|
If you are not installing the Service Binding Operator through Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM), you must install cert-manager on the cluster. Installing the cert-manager automates TLS certificates for Kubernetes and OpenShift workloads. Cert-manager ensures that the certificates are valid and up-to-date, and attempts to renew certificates at a configured time before expiry. You can install cert-manager by running the following command: |
-
You have access to a Kubernetes or an OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) cluster using an account with cluster-admin permissions.
-
You have the cert-manager installed on the cluster if you are not installing the Service Binding Operator through OLM.
-
You have installed the Helm CLI.
-
You have installed the
kubectlorocCLI.
Adding the Helm chart repository
-
Add the
service-binding-operator-helm-chartrepository to your local repository and name the repository as per your convenience:helm repo add service-binding-operator-helm-chart https://redhat-developer.github.io/service-binding-operator-helm-chart/Example output"service-binding-operator-helm-chart" has been added to your repositories -
Verify your Helm repository by listing it:
helm repo listExample outputNAME URL service-binding-operator-helm-chart https://redhat-developer.github.io/service-binding-operator-helm-chart/The output verifies that the
service-binding-operator-helm-chartrepository is added to your local helm repository.
Installing the Helm chart
-
Search the repository:
helm search repo service-binding-operator-helm-chartExample outputNAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION service-binding-operator-helm-chart/service-binding-operator 1.0.0 1.0.1 A Helm chart to deploy service binding operator -
Create a Helm chart release and specify the namespace required with the
--create-namespaceflag:helm install service-binding-operator-release \ service-binding-operator-helm-chart/service-binding-operator \ --namespace service-binding-operator --create-namespace -
Optional: If you wish to install the chart on the default namespace, remove the
--namespaceand--create-namespaceflags.As part of the Helm test, objects such as deployment, service binding resources, and secrets used for testing the Operator are deleted.
-
Optional: To view the resources created for testing, install the chart with the
keepTestResourcesflag value set totrue:helm install service-binding-operator-release \ service-binding-operator-helm-chart/service-binding-operator \ --namespace service-binding-operator --create-namespace \ --set keepTestResources=trueExample outputNAME: service-binding-operator-release LAST DEPLOYED: Mon May 16 09:15:16 2022 NAMESPACE: service-binding-operator STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 -
Verify that the chart is succesfully installed:
kubectl get pods --namespace service-binding-operatorExample outputNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE service-binding-operator-78c6444b4d-kswhk 1/1 Running 0 21s
Running a Helm test
|
If you are installing the chart on the Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) cluster, then perform the following steps to get appropriate Procedure
|
-
Create a
my-k-configsecret from yourkubeconfigfile and specify the required namespace:kubectl create secret generic my-k-config --from-file=kubeconfig=<PATH TO YOUR KUBECONFIG> --namespace service-binding-operatorExample outputsecret/my-k-config createdThe output verifies that the
my-k-configsecret is created. -
Run the Helm test and specify the namespace if applicable:
helm test service-binding-operator-release --namespace service-binding-operatorExample outputNAME: service-binding-operator-release LAST DEPLOYED: Mon May 16 10:44:53 2022 NAMESPACE: service-binding-operator STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: service-binding-operator-release-test Last Started: Mon May 16 11:01:10 2022 Last Completed: Mon May 16 11:01:22 2022 Phase: SucceededThe
Succeededphase from the output indicates that the Helm test has run successfully. -
Verify that the Helm test has run successfully:
kubectl get pods --namespace service-binding-operatorExample outputNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE service-binding-operator-release-test 0/1 Completed 0 4m28sThe output verifies that you have successfully installed the Service Binding Operator using a Helm chart and are able to bind your workload to backing services.
-
As a safety measure, delete the secret created and specify the namespace if applicable:
kubectl delete secret my-k-config --namespace service-binding-operatorExample outputsecret/my-k-config deletedThe output verifies that the secret you had created is now deleted.
Deleting the secret avoids exposing the secret credentials of the cluster to which you are connected.